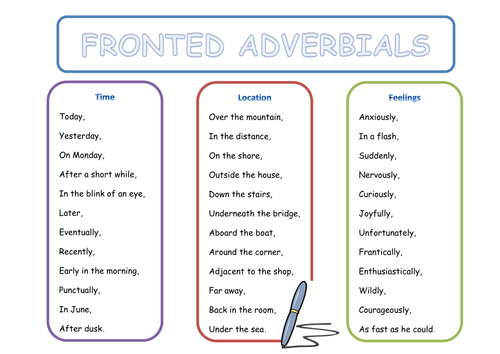
she defines it as: Word usage is how a word, phrase, or concept is used in a language. Lexicographers gather samples of written or spoken instances where a word is used and analyze them to determine patterns of regional or social usage as well as meaning.
She differentiate different words from one another because there are some words that has the same or almost the same spelling but differs with their meanings.
Word usage is really important since we are constructing different sentences or literary pieces, it a must for us to know the right word to use in a certain sentence for us to be able to convey our message effectively and properly.
Words were indeed tricky but it is the most important thing in the world, it can help us in almost everything that we do and using it properly can help us improve ourselves in different aspects of life.
So that's it you Guys, I hope I helped you with your Grammar Stuffs
Hope to see you on my next one. Bye :)